The Moon will eclipse Mars next week; how and when to see it

It’s not every day moon moves in front of a bright planet, but a likely once-in-a-lifetime event for parts of the US opens next week.
A rare second eclipse of Mars will occur on January 30, when the planet disappears from our view just past the left side of the Moon and reappears an hour later from the opposite side.
Patrick So, Observatory Program Manager Griffith Observatory in Los Angelessaid the viewing area is mostly limited to the US south, Mexico, Central America, northwestern parts of South America and most of the Caribbean.
While the time varies depending on where you live in the southern US, Mars will disappear from the sky of Los Angeles at 8:36 PM PT and then reappear on the other side of the Moon at 9:30 PM PT. Time will be later for areas further east in the US South.
“For other parts of the southern US, these times differ mainly due to the parallax of the Moon, and so you can’t see the Moon passing Mars further north,” So said.
If you look at the sky at around 8:00 PM PST, Mars and the waxing bulging moon will be separated by almost a quarter of a full moon. As Mars begins to fade from the dark side of the Moon, it will take the Moon about a minute to completely cover the planet’s finite diameter before disappearing.
“The eclipse is almost like an eclipse of Mars by the Moon,” So said.
This is because all the planets in the solar system rotate in approximately the same plane. Earth. As the planets move across the sky, they move along the ecliptic, the path followed by the sun, planets, and moon.
“Because the Moon is sort of close to the plane where all the planets move across the sky, it sometimes collides with the planet and moves in front of it, and so you get an eclipse,” So said.
Before the eclipse next week The last time the full moon passed in front of Mars was December 7, 2022.. If you think that’s not uncommon, two such coverages in less than two months at night are rare, Seo added.
The next Mars occultation, visible across most of the US, will occur on January 13, 2025.
“When I say they’re rare, it’s not as rare as a total eclipse that happens anywhere, averaging about 375 years,” So said.
The reason we see them less often, So added, is because they are found in different parts of the world.
“Sometimes these coverages happen during the daytime when we don’t see them,” he said. “We pay attention because it happens at night and we see it.”
The FOX Forecast Center said computer forecast models are showing a big up-and-down rotation over Southern California early next week. Cloud coverage in Los Angeles is forecast to be around 0%, but this number is expected to change as we get closer to the event.
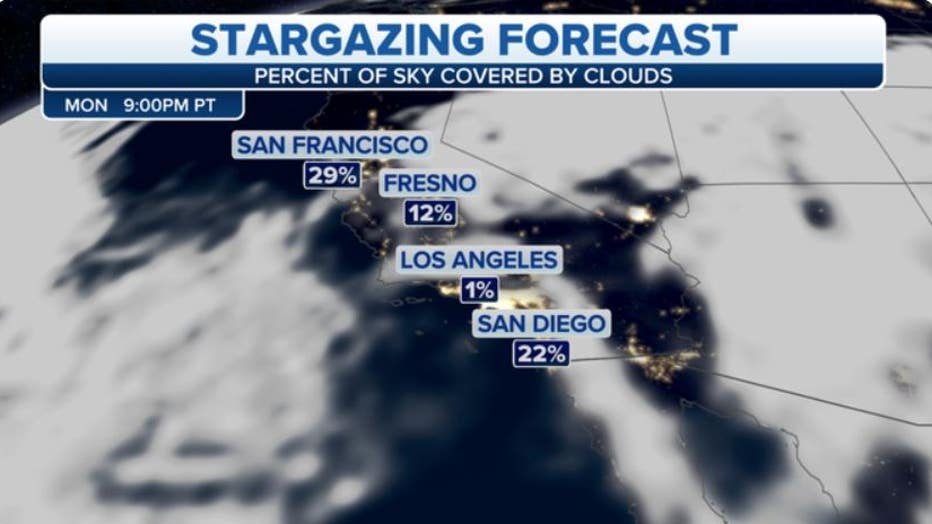
Under clear skies, the eclipse will be visible to the naked eye from anywhere in Southern California, according to the Griffith Observatory.
“You can really go out in the evening, and when it’s dark you can look directly over the constellation of Orion the Hunter. Above it and to its right is the constellation Taurus the Bull, and Mars is currently in this constellation. It is impossible not to notice him. It is the brightest reddish object in this region of the sky.”
It is safe to observe the eclipse without any eye protection. If you have binoculars, they can enhance and magnify the image of Mars and the Moon.
“If people have the opportunity to go outside and the sky is clear, just enjoy this spectacle,” Seo said. “It’s going to be another long wait until you see it happen again.”
On Monday, the Griffith Observatory will conduct a live online broadcast of the eclipse of Mars by the Moon. Click here to join the discussion.
Get updates on this story at FOXWeather.com.
Dallas Press News – Latest News:
Dallas Local News || Fort Worth Local News | Texas State News || Crime and Safety News || National news || Business News || Health News
texasstandard.news contributed to this report.










